ArgoCD has emerged as a leading GitOps tool, empowering teams to manage Kubernetes deployments declaratively with Git serving as the single source of truth. Known for its robust feature set, ArgoCD offers automated sync, rollback support, drift detection, advanced deployment strategies, and multi-cluster support. However, as organizations scale, several pain points and operational challenges surface.
Pain Points with Traditional ArgoCD Usage
– Technical Complexity : ArgoCD’s UI and CLI are designed for users with a strong technical background. Interacting with YAML manifests and understanding Kubernetes resource relationships require specialized knowledge, limiting GitOps workflows’ accessibility for less technical stakeholders.
– Operational Complexity : Managing ArgoCD across multiple clusters or environments introduces significant operational complexity. Teams must handle multiple ArgoCD instances, maintain consistent configuration, and coordinate deployments, which can become a bottleneck as service footprints grow.
– Pipeline Fragmentation : ArgoCD excels at syncing and monitoring Kubernetes resources but lacks built-in mechanisms for pre-deployment (e.g., image scanning) or post-deployment (e.g., load testing) tasks. This necessitates reliance on external tools or custom scripts, fragmenting the deployment pipeline.
– Manual Application Promotion : Promoting applications across environments (Dev → Test → Prod) is not natively streamlined, requiring manual orchestration or scripting.
– Multi-Cluster Management Challenges : As organizations adopt multi-cluster strategies, managing ArgoCD’s access, RBAC, and resource visibility becomes cumbersome, leading to fragmented workflows and potential security gaps.
ArgoCD MCP Server with Amazon Q CLI: Addressing the Challenges
The integration of the ArgoCD MCP (Model Context Protocol) Server with Amazon Q CLI revolutionizes the user experience by introducing natural language interaction for GitOps operations.
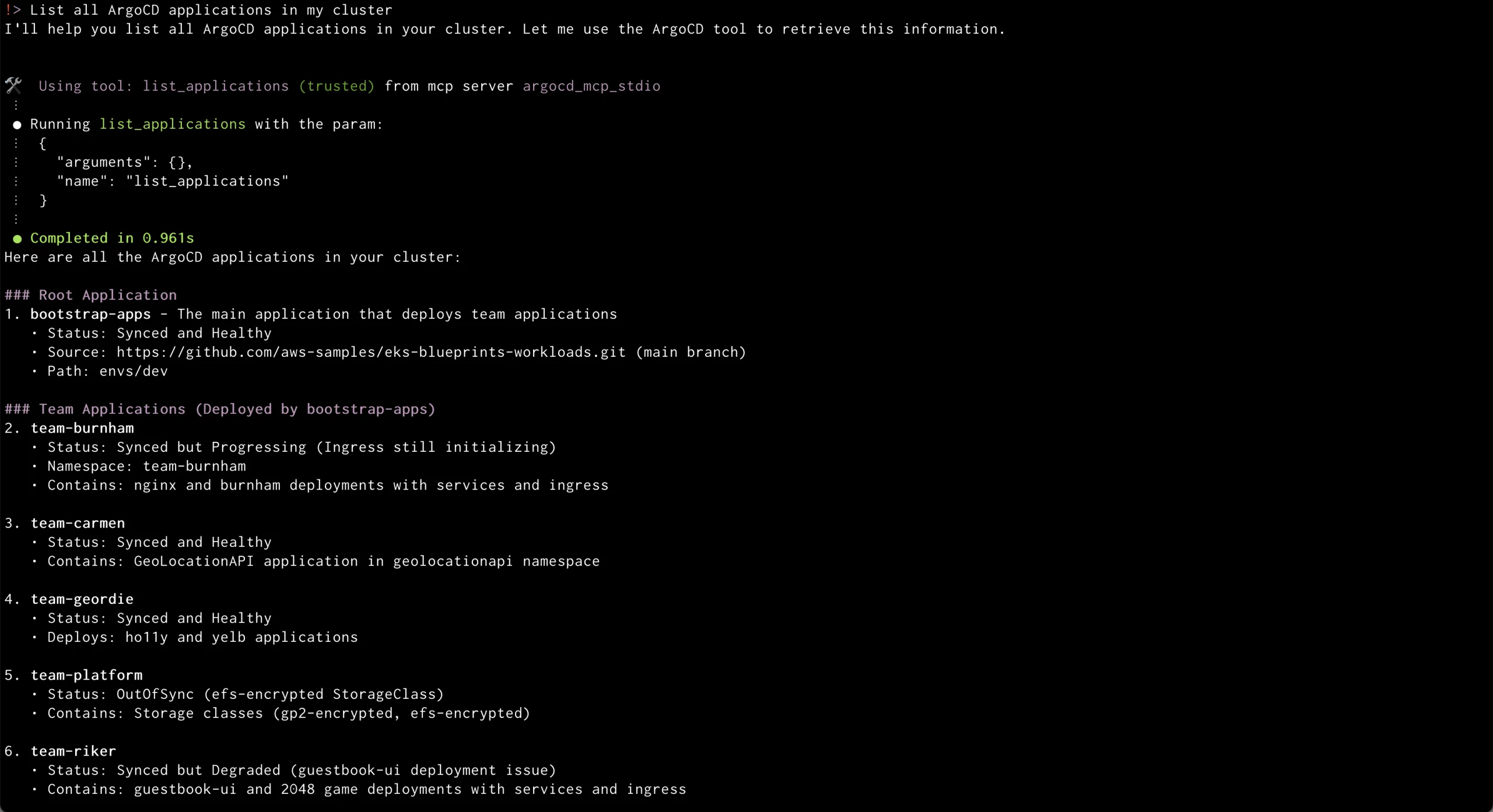
– Natural Language Commands : With MCP, users can manage deployments, monitor application states, and perform sync or rollback operations using plain conversational language. For example, users can ask, “What applications are out of sync in production?” or “Sync the api-service application,” and the system executes the appropriate ArgoCD API calls in the background.
– Democratized Access : This approach democratizes access to GitOps, enabling less technical team members to safely interact with deployment workflows.
– Simplified Management : Natural language interfaces abstract away the complexity of multi-cluster and multi-environment management. Users can query or act on resources across clusters without memorizing resource names, namespaces, or API endpoints.
– Enhanced Reliability : The MCP server handles authentication, session management, and robust error handling, reducing the need for manual troubleshooting and custom scripting.
– AI Assistants : The integration enables AI assistants and language models to automate routine tasks, recommend actions, and even debug issues, acting as virtual DevOps engineers.
Traditional ArgoCD vs. ArgoCD MCP Server with Amazon Q CLI
– User Interface : Traditional requires technical UI/CLI and YAML; MCP + Amazon Q CLI uses natural language.
– Access : Traditional is limited for non-engineers; MCP + Amazon Q CLI offers broad, democratized access.
– Multi-Cluster Management : Traditional is complex and manual; MCP + Amazon Q CLI is simplified and abstracted.
– Automation : Traditional requires scripting; MCP + Amazon Q CLI is AI/agent-driven and proactive.
Setting Up the Environment
Pre-requisites
– AWS account with appropriate permissions
– AWS CLI v2.13.0 or later
– Node.js v18.0.0 or later
– npm v9.0.0 or later
– Amazon Q CLI v1.0.0 or later
– EKS cluster (v1.27 or later) with ArgoCD v2.8 or later installed
Connecting to Your EKS Cluster
1. Use AWS CLI to update your kubeconfig: `aws eks update-kubeconfig –name
2. Verify ArgoCD pods: `kubectl get pods -n argocd`
3. Access the ArgoCD server UI locally using port forwarding: `kubectl port-forward svc/blueprints-addon-argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443`
Integrating with Amazon Q CLI
Create an Amazon Q CLI MCP configuration file to integrate with ArgoCD.
Once configured, natural language commands can manage ArgoCD applications, from listing applications to synchronizing and monitoring their status.
Managing cloud infrastructure through natural dialogue becomes more accessible and efficient, transforming teams’ focus from technical complexities to creating business value.
Note: This article is inspired by content from https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/devops/gitops-continuous-delivery-with-argocd-and-eks-using-natural-language/. It has been rephrased for originality. Images are credited to the original source.

Leave a Reply